Explain-Java-Array-masterskill
 |
| Java - Array |
An Array is collection of Similar type of data and element are store continousely in memory location,
"Java array is an object , which contain element of a similar data type, the element of an array are store in memory location."
Syntax :-
- Array in java is index-based the first element of the array is stored at the (0),zero th Index, 2nd element 1st index and so on.
Type of Java Array
There are two type of Array
- Single dimensional array
- Multi-dimensional array
1.Single Dimensional Array
Array is collection of similar data element, and storage data in memory location
For Example:-
If we are store the name of 50 student name then we are crete an array of string (datatype) that can store 50 name of student
string[]array=newstring[50]
Datatype.Arrayname[arraysize]
- Datatype- Primitive datatype-like-int, char, float, double, byte etc or java objects
- Array name- It is an identifier
For example
double[]dataHere, data is aaray that can hold value of type (double)
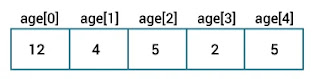
Initialize Array
int[]age={12,4,5,2,5};
2.Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. Each element of a multidimensional array is an array itself.
For example,
int[][] a= new int[3][4];
Here, we have created a multidimensional array named a It is a 2-dimensional array, that can hold a maximum of 12 elements
Remember, Java uses zero-based indexing, that is, indexing of arrays in Java starts with 0 and not 1.
Let's take another example of the multidimensional array. This time we will be creating a 3-dimensional array.
For example,
string[][][][] data = new string[3][4][2];
Here, data is a 3d array that can hold a maximum of 24 (3*4*2) elements of type String.
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};




Comments
Post a Comment